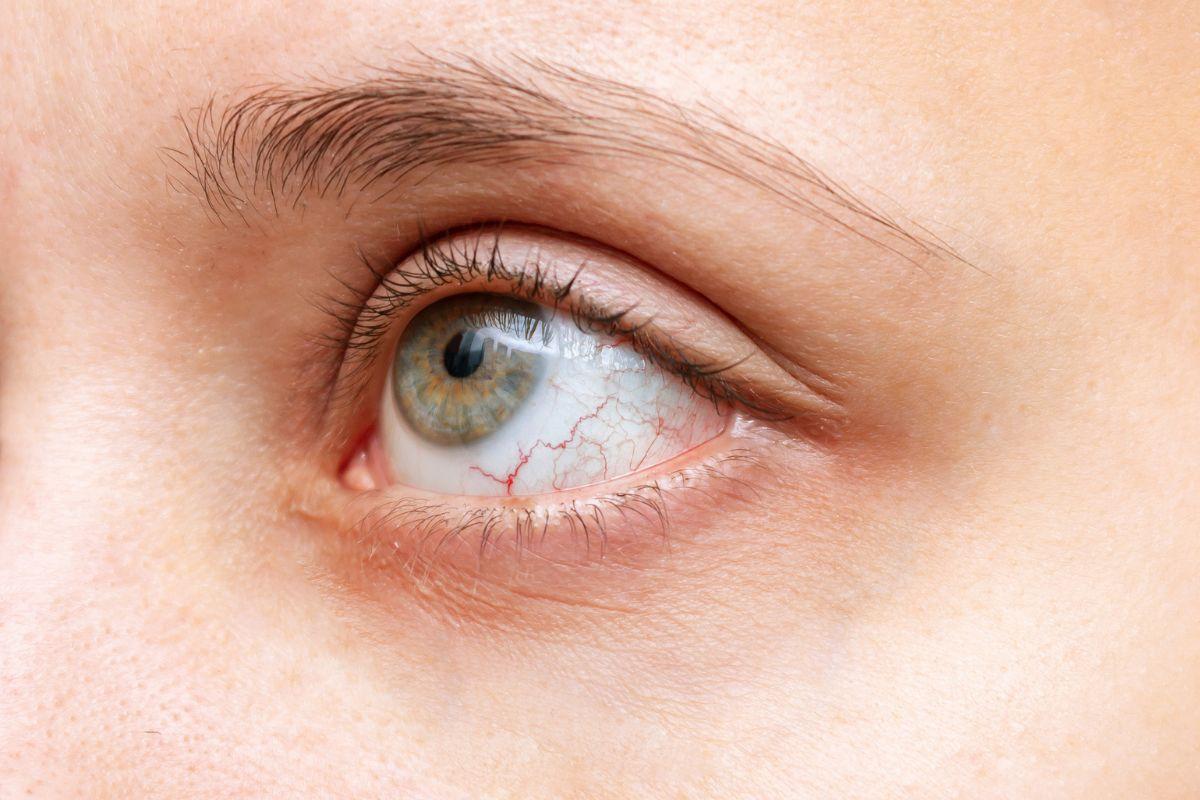
Eye problems can feel especially alarming. If you suddenly notice redness, pain, or blurred vision, it’s natural to feel worried. One possible cause is uveitis—an inflammation inside the eye.
Uveitis affects the uvea, which is the eye’s middle layer, and while it can be serious, the reassuring news is that with prompt diagnosis and treatment, most people recover well and protect their sight.Doctify connects patients with experienced ophthalmologists who can assess symptoms quickly and provide tailored treatment.
What is Uveitis?
Uveitis simply means inflammation of the uvea, which includes the iris (the coloured part of your eye), the ciliary body (which helps focus the lens), and the choroid (the blood vessel layer at the back of the eye)
There are different types:
- Anterior uveitis: affects the front of the eye
- Intermediate uveitis: affects the middle structures
- Posterior uveitis: affects the back of the eye
- Panuveitis: involves all layers of the uvea
Where the inflammation occurs helps determine the right treatment.
Causes of Uveitis
Uveitis has many possible causes. Sometimes a clear trigger is identified, while in other cases it remains unexplained (idiopathic). Common causes include:
- Autoimmune conditions: such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, or ankylosing spondylitis
- Infections: including herpes, tuberculosis, syphilis, or toxoplasmosis
- Eye injury or surgery: trauma can trigger inflammation
- Idiopathic cases: no specific cause found, yet treatment is still effective
The important point: treatment can begin promptly even if the exact cause isn’t immediately clear.
Symptoms patients might notice
Uveitis can develop suddenly and may include red, painful eyes, blurred or reduced vision, a sensitivity to light (photophobia), or floaters (dark spots or shapes drifting in vision).
Because these symptoms overlap with other eye problems, it’s always best to seek specialist care quickly.
How uveitis is diagnosed
An eye specialist will usually carry out a few tests to help in diagnosing uveitis. They would perform an eye examination with a slit lamp to check for inflammation. They may perform imaging tests such as OCT or fundus photography (especially for posterior uveitis). If an autoimmune disease or infection is suspected, the provider may order blood tests or X-rays.
These tests are safe and help rule out other conditions while guiding treatment.
Treatment options for uveitis
Treatment is tailored depending on the type and cause of uveitis. Options may include:
- Corticosteroid eye drops: often the first-line treatment for anterior uveitis
- Oral or injected steroids: used if inflammation is deeper or more severe
- Immunosuppressive therapy: medicines that calm an overactive immune system, for patients needing long-term control
- Antibiotics or antivirals: prescribed if an infection is the underlying cause
The goal of all treatments is to reduce inflammation, relieve symptoms, and protect vision.
Living with and managing uveitis
Patients with uveitis can help protect their sight by implementing easy to-do lifestyle changes and adhering to the prescribed treatment plan. Your best chance of success can be achieved by attending your regular follow-up appointments, using drops or tablets exactly as prescribed, and wearing sunglasses to reduce light sensitivity.
With early treatment and ongoing monitoring, most people maintain good long-term vision.
Possible complications if untreated
If ignored, uveitis can lead to more serious problems that can persist for longer and impact your quality of life. Some examples include glaucoma (high pressure inside the eye), cataracts (clouding of the lens), and even permanent vision loss.
The reassuring news is that these complications are largely preventable when treatment is started early and treatment plans are followed.
When to see an eye specialist urgently
Seek immediate help if you notice:
- A sudden, painful red eye with blurred vision
- New floaters or flashes of light
- Rapid worsening of symptoms
Early specialist assessment can prevent long-term damage. If needed, you can easily connect with a trusted eye specialist on Doctify.
Conclusion
Uveitis can be worrying, but it is manageable with the right treatment. Prompt care from an eye specialist makes all the difference in preserving vision and avoiding complications.
If you notice unusual changes in your eyes, don’t wait—book an appointment with a specialist via Doctify. With proper therapy and follow-up care, most people with uveitis go on to live full, active lives with healthy vision.
Find the right specialist for you. Doctify uses verified reviews so you can make the best decision for your healthcare.

Find the best ophthalmologists in the United Kingdom or search for specialists globally:
- Ophthalmologists in Ireland
- Ophthalmologists in Australia
- Ophthalmologists in the United Arab Emirates
- Ophthalmologists in Germany
Medically Reviewed
Last reviewed on 19/09/2025