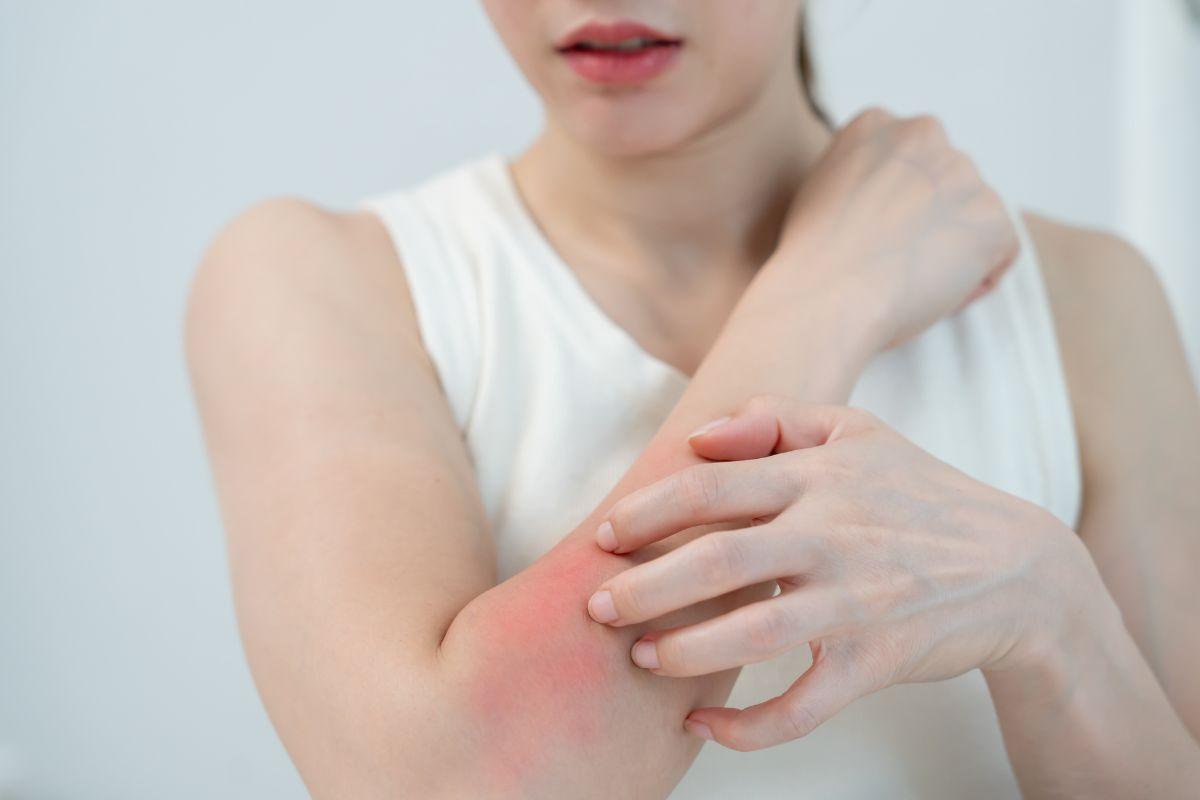
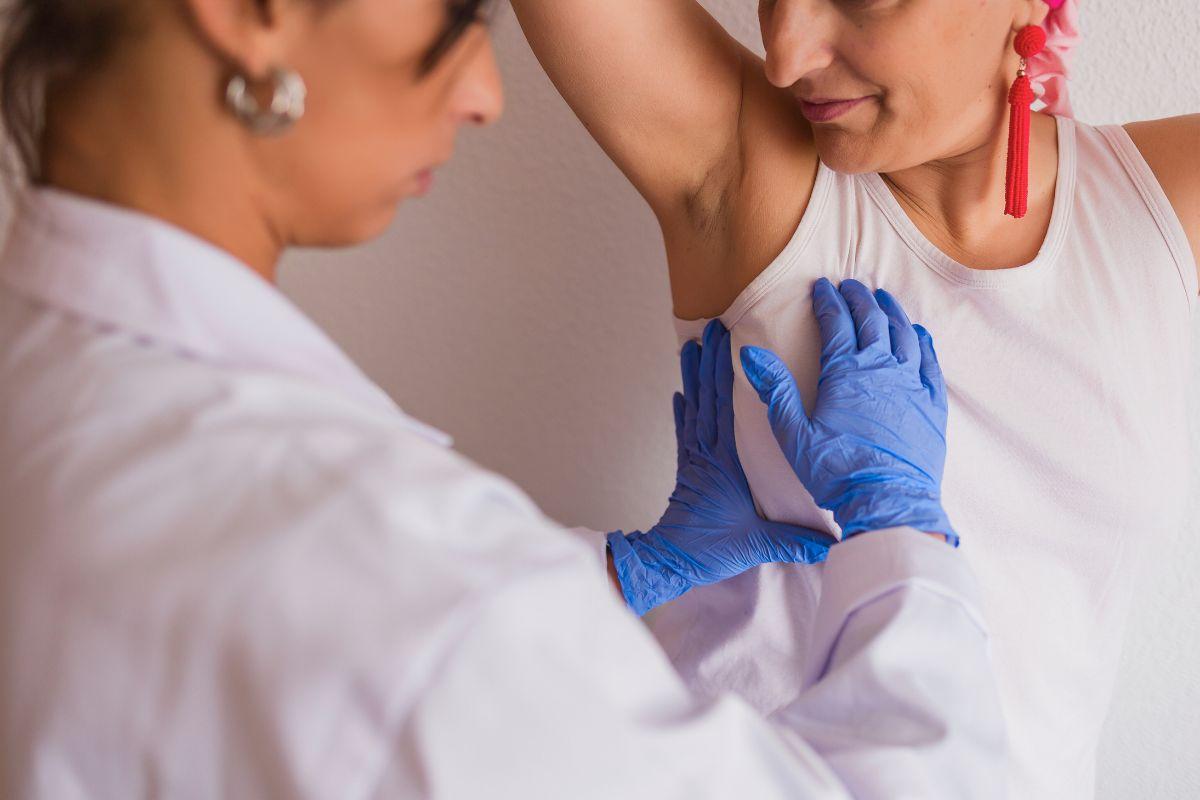
Frequently, many people experience unexplained rashes or skin irritations, also known as skin allergies and contact dermatitis. These skin allergies can be frustrating and difficult to pinpoint. A patch test, performed by a dermatologist, can help identify what’s triggering your reaction — from skincare products to metals or fragrances. Doctify connects patients with trusted dermatologists who perform patch testing safely and accurately.
What is a patch test?
A patch test is a diagnostic test used to find out if your skin reacts to specific substances that cause contact dermatitis. The patch test is different from a prick or blood allergy test, since it identifies delayed allergic reactions on the skin, not immediate immune responses. This test is commonly prescribed when the usage of creams, soaps, or cosmetics cause persistent irritation.
What is contact dermatitis?
Contact dermatitis is a condition in which skin reacts to substances that, in direct contact, irritate skin or trigger an allergic reaction. It is not contagious and patients experience symptoms like redness, itching, and blisters, which appear where the skin touched the irritant or allergen. Common causes include poison ivy, nickel in jewelry, and harsh chemicals in soaps or cleaning products.
Common triggers detected by patch testing
Patch testing can detect a wide range of triggers, with standard series typically testing 20–40 common allergens, but sometimes up to 80. Among the most common triggers detected are:
- Metals such as nickel or cobalt (often in jewellery or zips).
- Fragrances and preservatives in skincare or household products.
- Rubber chemicals (in gloves or elastic materials).
- Hair dyes and cosmetic ingredients.
- Topical medications and adhesives.
Who should consider a patch test
Below are the recommendations of whom should have a patch test:
- People with recurrent or chronic rashes that don’t clear despite treatment.
- Those with suspected contact dermatitis from daily products or workplace materials.
- Patients with eczema that worsens with certain lotions or soaps.
- Anyone advised by their dermatologist after unexplained skin allergy episodes.
How the patch test works
The patch testing is a very easy procedure. First, small amounts of potential allergens are applied to the back using adhesive patches. Patches will stay in the place for about 48 hours. After removal, the dermatologist checks the skin for redness or irritation at each site. Finally, a second reading after another 24–48 hours confirms any delayed reactions.
What the results mean
Interpreting the results is simple. A positive reaction is shown as a mild red or itchy patch, indicating sensitivity to that substance. A negative result means no reaction to the substance was observed, evidencing no skin changes. The dermatologist will be in charge of explaining what substances to avoid and how to read product labels moving forward.
What to expect during and after the test
The process is generally painless, but mild itching or redness in the areas where the reaction was positive is common. Patients should avoid washing the back or sweating heavily while the patches are on. Once results are known, you’ll receive a list of safe alternatives from your dermatologist for your skincare or daily routine.
Treatment and management after a positive test
Here are the are our recommendations for treatment and management after a positive test:
- Avoid contact with identified triggers as much as possible.
- Use hypoallergenic products recommended by your dermatologist.
- Manage flare-ups with prescribed emollients, topical steroids, or anti-inflammatory creams.
- Ongoing follow-up may help track whether avoiding triggers improves skin health.
When to see a dermatologist
Please contact a dermatologist if you are experiencing any of the following:
- If your rash persists beyond a few weeks.
- If over-the-counter creams make irritation worse.
- If you suspect a work-related or cosmetic-related allergy.
- If you have unexplained skin allergy episodes.
- If you experience eczema that worsens with certain lotions or soaps.
Doctify can help book an appointment with an experienced dermatologist for accurate diagnosis and safe patch testing.
Conclusion
Skin allergies and contact dermatitis can be exasperating. Nevertheless, a patch test can uncover the root causes, since it helps identify specific irritants and allergens in the skin like metals, fragrances, and preservatives that other allergy tests cannot. Patch tests reveal delayed hypersensitivity reactions by observing a local skin reaction after the allergens have been on the skin for 48 hours. Early testing prevents repeated exposure and long-term skin irritation, helping you regain comfort and confidence. We invite you to use Doctify to find a qualified dermatology specialist for personalised testing and treatment options.
Find the right specialist for you. Doctify uses verified reviews so you can make the best decision for your healthcare.

Feel free to consult a dermatologist through Doctify for personalised advice whenever you want, we will be happy to help you! Find the best dermatologist in the United Kingdom or search for the best specialists globally:
- Dermatologist in the United Arab Emirates
- Dermatologist in Germany
- Dermatologist in Austria
- Dermatologist in Ireland
- Dermatology in Australia
Medically Reviewed
Last reviewed on 21/10/2025